Student loan repayment tool revamp
We’re always looking for ways to improve the information and tools we make to help consumers. Today, we’re launching improvements to the Repay Student Debt feature in our Paying for College tool. This helps current and former students navigate repayment options by providing relevant resources and advice based on their student loan situation.
Our first version of the feature included a set of decision tree questions and several scenario-based information modules. We knew this would help consumers right away, but we also knew we’d need to make improvements as we received user feedback. We reviewed usage data and user feedback and made the following improvements in time for the end of the school year:
- An introduction that helps student loan borrowers understand the benefit of the tool
- A new decision tree interface
- Revised content that is more direct and uses less jargon
- Updated visual design that directs users to next steps and actions they can take after using the Repay Student Debt tool
According to usability testing, the Repay Student Debt feature was effective but presented significant usability challenges. We learned that the front page didn’t give users a clear understanding of the features, and the question-and-answer pathway was confusing. In addition, we ran our own analysis of the content layout and found that we weren’t clearly directing users to specific action steps they could take after using the tool. For example, our web traffic data showed that 40 percent of users ended their experience at a module about income-based repayment, a student loan repayment program that allows borrowers to limit the amount they must repay each month based on their income. However, few users took the next step and clicked through to the repayment program website where they could enroll. Our improvements make these kinds of next steps clearer.
Improved decision tree interface
While we’re excited to see how all of the changes will create a better experience for consumers dealing with student loan questions, the centerpiece of our update is the new decision tree interface.
In the original version of the tool, each question disappeared once it was answered, leaving users feeling disoriented and uncertain. During usability testing for that version, users asked questions like, What are all these questions about? What’s the relationship between this question and the one I just answered? Wait, what if I want to change my answer to a question?
In addition, the actual question text was often removed from the answer options by a block of informational text. Our testing showed that users got bogged down or exited in search of further details, failing to reach the helpful information at the end of the decision tree.
We made two critical user interface changes:
-
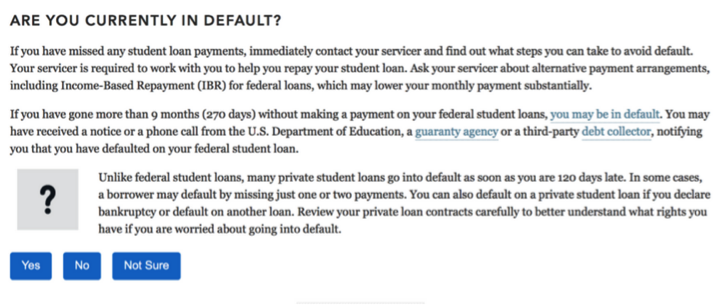
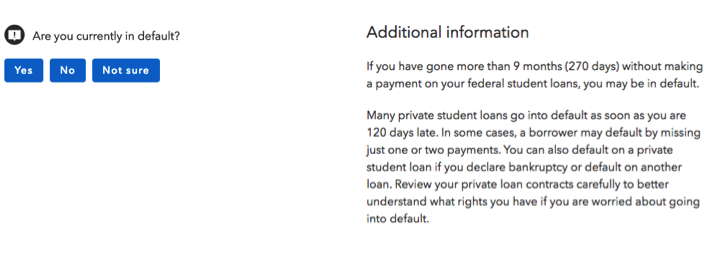
Focus on the question and answers by reducing and moving any additional information to the right side. An example decision tree question:
Before:
After:
-
Keep the answered questions on-screen, allowing users to see what information they’ve provided and to easily change any answers if necessary.
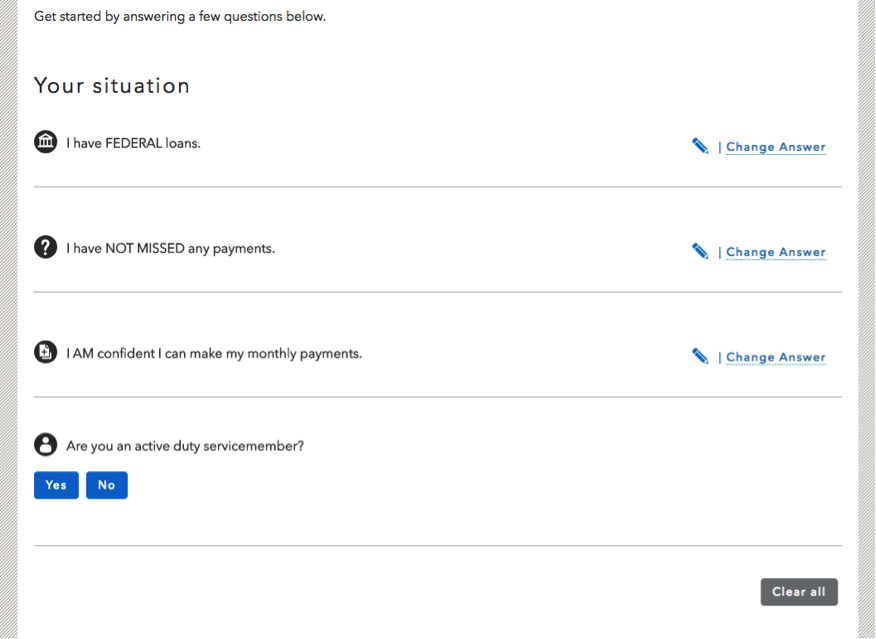
A better experience for consumers using our tools and better code go hand-in-hand. Not only do we believe this new decision tree interface is easier for consumers to use, it’s also easier for our developers to maintain, thanks to a modular plugin called Decision Stacker that we developed internally.
To make it easy to change the decision tree in the future, Decision Stacker maps every button (and potential decision) to a simple JavaScript object. By changing the object, a developer can change the flow of the decision tree. The object also powers Decision Stacker’s unique “Change Answer” option that is present on every question, allowing a user to essentially “rewind” their choices to any previous decision point. As we test Decision Stacker further, we’ll release the code on GitHub so others can use it and contribute to it, too.
We hope you check out the improved Repay Student Debt feature on Paying for College and let us know what you think in the comments below.
